As an Amazon seller, protecting your intellectual property (IP) and respecting the rights of others is crucial for maintaining a good account standing and a positive reputation. However, navigating the complexities of intellectual property violations on Amazon can be confusing. This blog post aims to demystify the different types of Amazon intellectual property violations you might encounter and guide you on how to avoid them.
What Is Intellectual Property (IP)?
Intellectual property (IP) includes non-physical assets created through human creativity, like artwork, logos, and brand names. Companies actively identify and protect these assets due to their immense value in a knowledge-driven economy.
Since creating IP requires significant expertise and time and represents an organization’s unique identity, organizations protect their IPs against unauthorized use.
IP not only adds immense value to a company but can even surpass the worth of physical assets, providing a strong competitive edge. For this reason, companies place high importance on both using and protecting their intellectual property.
For instance, you can readily recognize companies like Nike, Apple, McDonald’s, etc., by just looking at their brand logos. So their logos are invaluable IP assets for these companies.

What Is IP Violation on Amazon?
An IP violation on Amazon happens when a seller is accused of infringing on someone else’s intellectual property rights, such as using copyrighted content, trademarks, or patented designs without permission.
There are three main types of IP rights on Amazon:
- Trademarks: A trademark is a recognizable design, phrase, word, or symbol that identifies a specific brand or product source. For instance, the swoosh symbol belongs to Nike, and the golden arches belong to McDonald’s.
- Copyrights: A copyright protects original works of authorship, including literary works, musical works, artistic works, films, and computer software. Product descriptions, images, and even unique product designs can be copyrighted.
- Patents: A patent grants the inventor exclusive rights to an invention for a specific period. This can include the functionality or the unique design of a product.
Also Read: Why Every Amazon Seller Should Audit Their Account?
What Are the Common Intellectual Property Issues on Amazon?
Common intellectual property (IP) problems on Amazon include using someone else’s brand name without permission, copying images or text, selling fake products, copying patented designs, and reselling products through unauthorized channels.
These issues can lead to listing removal, account suspension, or even legal action. Here’s a list of the most common Amazon IP issues:
- Trademark Infringement: This occurs when you use a brand name, logo, slogan, or other protected trademark without permission from the rights holder. This can happen in your product listing title, description, keywords, or even in your product images if they feature a brand logo you don’t own.
- Copyright Infringement: Using copyrighted material without permission is another major IP violation. This includes using copyrighted product descriptions and images, or even copying another seller’s unique product design.
- Selling Counterfeit Products: Counterfeiting involves selling a product that is an imitation of a genuine brand product. Counterfeiting is a serious offense and can lead to account suspension and legal repercussions.
- Patent Infringement: Selling a product that infringes on a valid patent is another IP violation. This can be more complex but generally involves replicating the functionality or unique design features protected by a patent.
- Gray Market (Parallel Imports)
This involves selling genuine products that were meant for sale in a different country or region, without the brand owner’s approval. - Listing Hijacking
This occurs when a seller adds their product to an existing branded ASIN, even though their product is different or generic. This can harm the brand and mislead customers.
Amazon takes IP rights violations very seriously. The platform has a system in place for rights owners to report suspected infringements. If Amazon receives a valid IP complaint against your listing, they may remove your listing, suspend your account, or even take legal action.
Also Read: The Most Common Reason for Amazon Account Suspension
Types of Intellectual Property Violations on Amazon
Here’s a breakdown of the types of Amazon’s Intellectual Property (IP) violations and the complaints sellers may encounter. You can find these intellectual property violations in your Account Health Dashboard in Seller Central.
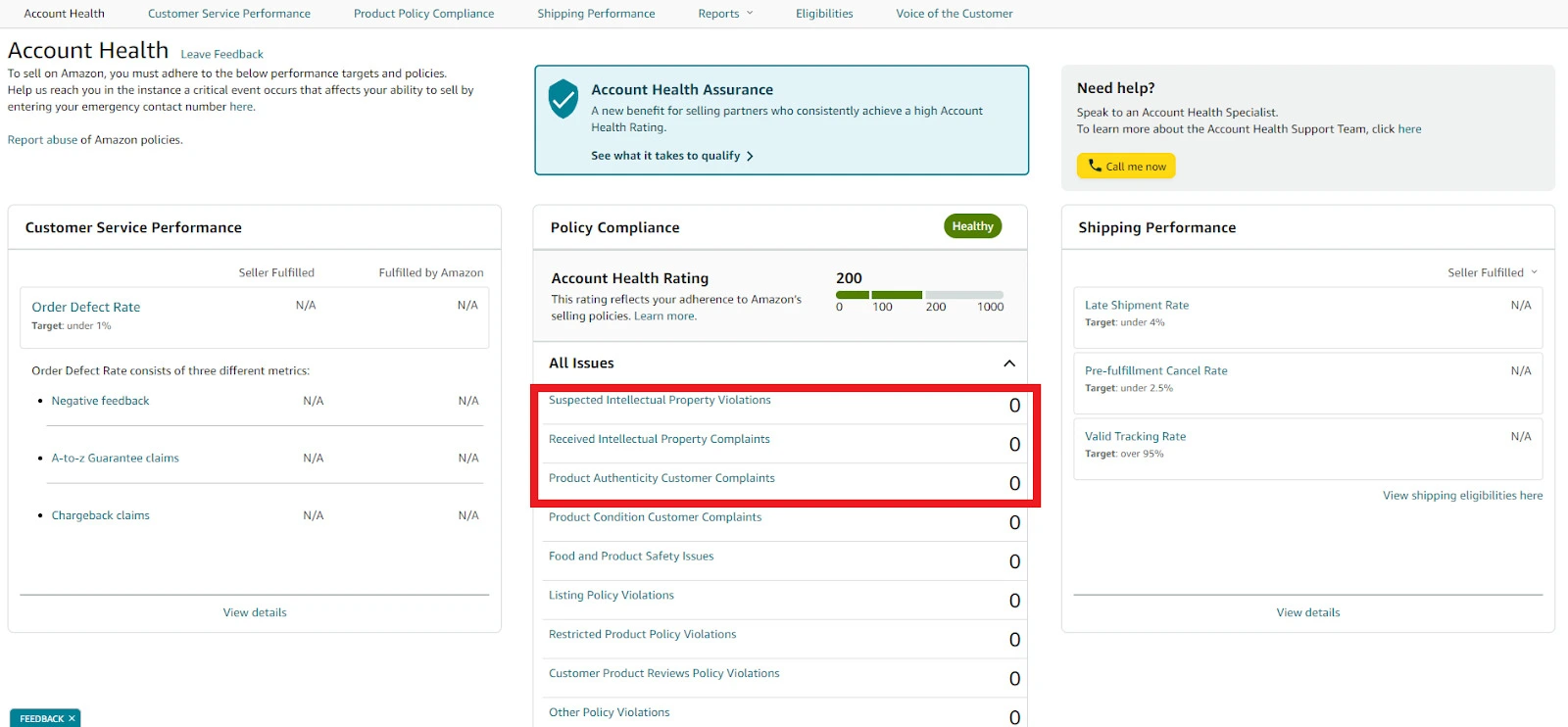
1. Suspected Intellectual Property Violations
Amazon may flag listings if you use a brand name you don’t own to sell or describe your product, even if you don’t misuse their logo or branding directly.
For example, using phrases like “compatible with iPhone” or “better battery life than Samsung Galaxy” can trigger Amazon’s system to deactivate the listing for potential trademark issues.
So avoid using brand names in listings unless you have permission or are an authorized reseller. Stick to generic terms to describe compatibility.
2. Received Intellectual Property Complaints
These occur when a brand files an official complaint with Amazon, usually because you’re selling their product without permission, or the product source lacks verification.
For instance, selling a popular brand of sunglasses sourced from a wholesaler who isn’t authorized by the brand could result in a “counterfeit” complaint.
If faced with a complaint, reach out to the brand to request a complaint withdrawal or provide Amazon with documentation (like invoices) to prove your product source.
3. Product Authenticity Customer Complaints
Counterfeit complaints from customers can arise if the products you sell are found to be fake or faulty.
For example, sourcing products from platforms like Alibaba without verifying authenticity may result in counterfeit complaints, especially if customers receive poor-quality or imitation items.
Therefore, always verify suppliers and request authenticity documentation to prevent counterfeit issues and maintain customer trust.
How to Avoid IP Complaints on Amazon?
An Amazon IP complaint is a way for brand owners to protect their intellectual property, like trademarks or copyrights, by reporting sellers who may be selling their products without permission on Amazon. When a brand files this complaint, they aim to stop other sellers from listing products they believe infringe on their IP rights.
If Amazon reviews and accepts the complaint as valid, they may take down the listed product or even suspend the seller’s account. This helps brands control who can sell their products on Amazon and prevent unauthorized listings.
Here are some key steps you can take to avoid IP claims on Amazon:
- Do your research: Before listing a product, thoroughly research any brand names, logos, or designs associated with the product. Make sure you have the necessary permissions to use any intellectual property.
- Source from authorized distributors: If you are dropshipping or reselling branded products, ensure you are sourcing them from authorized distributors to avoid selling counterfeits.
- Create your own content: Use your own product descriptions and images. Don’t copy content from other sellers’ or brand websites.
- Be mindful of keywords: When choosing keywords for your products, avoid using brand names or trademarks that you don’t own.
- Stay informed: Keep yourself updated on Amazon’s IP policies and best practices. Amazon Seller Central is a valuable resource for information on this topic.
Ensuring authenticity, verifying sources, and using careful language in product listings are essential for staying compliant and avoiding these IP issues on Amazon.
How Can I Set Up IP Alerts for My Amazon Seller Account?
Setting up Intellectual Property (IP) alerts for your Amazon Seller account can significantly reduce the risk of account health issues. One of the most effective ways to do this is by using third-party Chrome extensions such as Seller Assistant’s IP-Alert tool. These extensions scan Amazon product pages for previous IP complaints and flag high-risk brands or ASINs with a visible warning (often a red triangle), helping you avoid problematic listings before sourcing inventory.
How to Set Up IP Alerts
1. Install a Browser Extension: Download a trusted IP monitoring extension (such as IP-Alert) from the Chrome Web Store.
2. Create an Account: Register on the provider’s website (for example, Seller Assistant) to activate the extension and link it to your account.
3. Analyze Product Pages: After installation, open any Amazon product page. The extension will automatically display alerts if the brand or ASIN has a history of IP complaints, authenticity issues, or policy violations.
4. Enable Amazon Policy Notifications: Inside Amazon Seller Central, go to Settings, click Notification Preferences, and make sure email alerts are enabled for policy violations and performance notifications.
Best Practices for Amazon IP Alerts
- Use Third-Party IP-Alert Tools: You can use third-party tools and extensions that identify potential intellectual property complaints, restricted product risks, and authenticity flags directly on listing pages.
- Research Before Sourcing: For best results, use IP alerts during your product research phase to avoid sourcing from brands that frequently file IP claims.
- Monitor Account Health Dashboard: Regularly monitor your Account Health Dashboard in Seller Central for any official warnings related to intellectual property, inauthentic claims, or product safety concerns.
What Is the Amazon IP Accelerator Program?
The Amazon IP Accelerator is a program designed to help brands protect their intellectual property (IP) and get faster access to Amazon’s powerful Brand Registry protections. Normally, to join Amazon Brand Registry, you must already have a registered trademark, and this process can take months or longer in some countries.
The IP Accelerator fast-tracks this by connecting you with a vetted network of trusted legal service providers (mostly IP law firms) that can help you create and file your trademark application at competitive rates.
With the IP Accelerator:
- You get expert legal support for trademark searches, filing, and other IP services.
- Your trademark application can be filed quickly and professionally through approved providers.
- Once your application is filed and pending, you can enroll in Amazon Brand Registry sooner, unlocking brand protection tools even before official trademark approval.
Brand Registry brings benefits like enhanced control over product listings, extra tools against counterfeits, and more brand-building options on Amazon.
Can Small Businesses Benefit From the Amazon IP Accelerator Program?
Yes, small businesses can benefit a lot from the Amazon IP Accelerator program. It is made to help small and medium businesses protect their brand and register a trademark at affordable, fixed prices.
The biggest benefit is that you can join Amazon’s Brand Registry soon after your trademark application is filed. You do not have to wait months for full approval. This gives you early access to tools like A+ Content, Brand Analytics, and better protection against counterfeit sellers.
Key Benefits for Small Businesses:
- Faster Access to Brand Registry
Once a law firm files your trademark through the program, you can apply for Brand Registry right away. You don’t have to wait for the final trademark approval. - Lower, Fixed Legal Costs
Amazon works with trusted law firms that offer set prices. This makes it easier for small businesses to afford professional trademark help. - Better Brand Protection
You get tools that help remove copycats and fake products. This protects your brand and builds customer trust. - Professional Legal Help
The approved law firms guide you through the trademark process and make sure everything is done correctly. - Help with International Growth
You can also apply for trademarks in other countries, which makes expanding to global Amazon marketplaces easier.
What Are the Steps to Apply for the Amazon IP Accelerator?
Enrolling in the IP Accelerator program is straightforward if you already have an Amazon selling account. Here’s how it works:
1. Log in to Seller Central: Use your Amazon Seller Central account. If you don’t have one, create an account first.
2. Open the IP Accelerator Page: From the main menu, go to Apps & Services, click Explore Services, and select IP Accelerator.
3. Choose a Service Provider: You’ll see a list of vetted legal firms. Review their profiles and choose the one that fits your needs.
4. Submit Your Request: Click Contact Provider, fill in your details, and click Submit Request. The provider will usually respond within a couple of business days.
5. File Your Trademark: Work with the chosen provider to search and file your trademark application in the relevant trademark office.
6. Enroll in Brand Registry: Once your trademark application is filed and pending, you can enroll in Amazon Brand Registry and access its protections.
Conclusion
By understanding the different types of IP violations on Amazon and taking proactive steps to avoid them, you can protect your account and your reputation while ensuring a smooth selling experience on the platform. Remember, respecting intellectual property rights is not only essential for following Amazon’s policies but also for building trust with your customers and fostering a fair and competitive marketplace for all.
Got More Questions?
Stay calm and address the issue promptly. Amazon will typically provide details about the alleged violation in the notification. Carefully review the information and identify the product or listing in question.
Ignoring an IP violation notification can have serious consequences. Amazon may take action such as:
- Removing your listing
- Suspending your selling privileges
- Withholding your funds
There’s no built-in tool for pre-screening listings. However, you can minimize risks by:
- Avoiding brand names, logos, or copyrighted material you don’t own.
- Using a plagiarism checker for your product descriptions.
- Sourcing from authorized distributors if reselling branded products.
Report the infringing listing to Amazon. You’ll typically need to provide proof of your brand ownership (trademark registration) to facilitate the removal of the counterfeit listing.
For complex situations or if you plan to sell a product that might touch upon trademark or patent issues, consulting with a lawyer specializing in IP is highly recommended.
Yes, the rights owner of a trademark, copyright, or patent can pursue legal action against you if they believe you have infringed on their intellectual property rights.
If you believe the claim is inaccurate, you can file an appeal with Amazon. This typically involves providing evidence to support your claim. Here are some things you can include:
- Proof of independent creation (e.g., drafts, design sketches) for your product or content.
- Documentation showing you obtained a license to use the copyrighted material (if applicable).
- Evidence that the complaining party doesn’t hold a valid copyright for the element in question.






